By Jason Shea M.S., CSCS, PICP IV
Gut Health and Probiotics
- Did you know that probiotics have been linked to improving testosterone and thyroid hormone?
- How about probiotics and healthy skin and shiny hair?
- Wound healing?
- Muscle growth?
- Fending off obesity?
- Cardiometabolic disorders?
- Cancer?
- And last but not least…. Longevity?
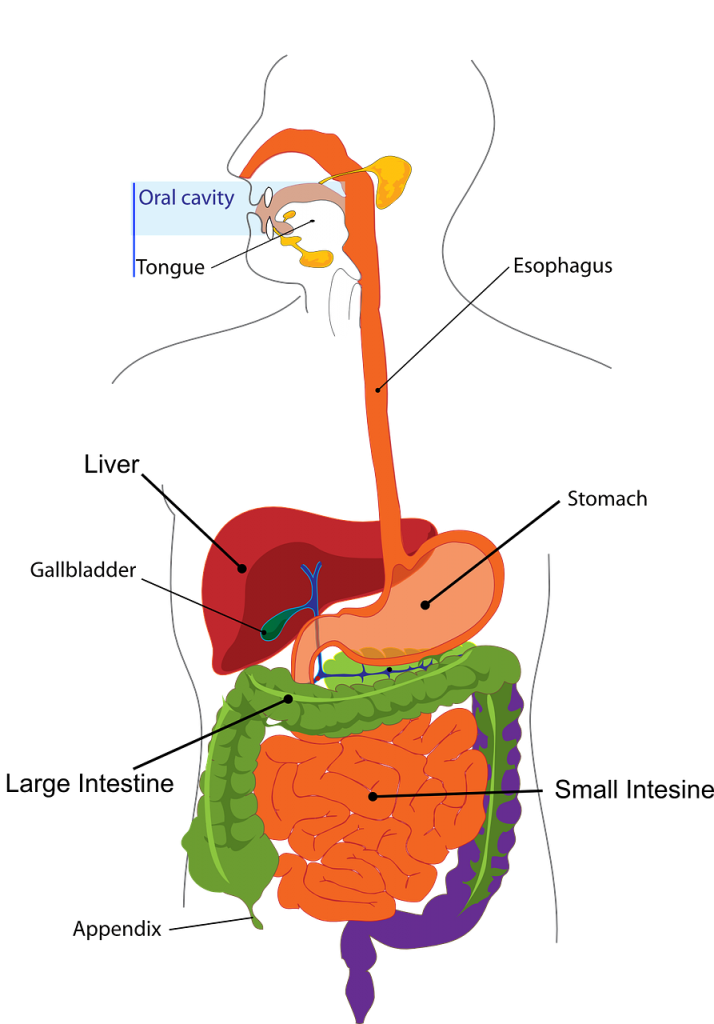
A study from 2008 revealed that something called the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) represented nearly 70& of the entire immune system. The same study also found that roughly 80% of immunoglobulin A cells were also located there (12).
Think of how impactful this knowledge is to our health? A healthier gut can lead to a stronger immune system. A stronger immune system may to lead to greater healthspan and longevity. Research on centenarians has found that those who age “well” often have healthier and more adaptable gut microbiota composition (3).
In her 2016 study on microbiota and healthy aging, renowned researcher from MIT, Dr Susan Erdman found that microbes prime the immune system and can positively impact FoxN1 and central nervous system hormones (11).
Let’s go over some of the general benefits associated with probiotics, then we will look at specific strains and some of the products they are found in.
The Glow of Health

When you think of a person who has a “glow of health” what comes to mind? Radiance. Vibrant. Upbeat. Healthy.
How about more specific physical characteristics? Healthy skin texture and tone. Healthy shiny hair. Lean, healthy muscles. Clear eyes. Good dental hygiene. Etc.
This term, as it relates to human health and probiotics/gut microbiota, was coined by Dr. Susan Erdman. In her groundbreaking research she discovered numerous health benefits associated with probiotic ingestion including:
- Improved wound healing (6)
- Healthier, more shiny hair (6)
- Less skin inflammation (6)
Other studies by her and her team have found:
Testosterone Boost
No matter what type of diet the mice were eating, high fat, high salt, high sugar, if they were ingesting the probiotic microbe Lactobacillus Reuteri, their levels of circulating testosterone increased significantly (8). I Wonder when they are going to start adding certain probiotic strains to testosterone boosting supplements?
Obesity blocker?

Did you know that eating probiotics can block something called the gut microbiota-immunity-obesity- axis? Neither did I, until I read Dr. Erdman’s 2013 study. In this study, they found that mice eating a Western Diet, or fast food diet if you prefer, were able to stay significantly leaner if they consumed the probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri.
They found that ingestion of this probiotic was enough to change the pro-inflammatory immune responses resulting from the fast food diet. This prevented abdominal fat from accumulating, and in turn, kept the mice lean no matter their diet (7).
Now, this is not a free pass to eat all the junk and fast food you want. The bacteria in your gut need healthy fuel to maintain their healthy status.
Tip: Healthy gut bacteria can create cravings for certain healthy foods. Unhealthy gut bacteria can create cravings for certain unhealthy foods.
Thyroid Hormone and Increased Activity Levels
Mice taking the probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri used the food they ingested toward energy for enhanced activity levels rather than being stored as fat. The mice ingesting the probiotic had higher levels of thyroid hormone, which regulates energy usage and fat storage (9).
Potential links to Cancer?
According to their 2015 study, Gut Bacteria and Cancer, “Emerging evidence shows that microbe interactions with the host immune system impact diverse aspects of cancer development and treatment. Microbe-based therapies may ultimately be used to reinforce host immune balance and extinguish cancer for generations to come (10).”
If you have not seen her research or watched any of her presentations, here is the link to her lab. Also, check out her presentation at the 2019 Harvard NORC Summit on Longevity.
More potential health impacts of probiotics
Blood pressure
When sodium starts to accumulate in your bloodstream your heart and circulatory system need to work a lot harder to pump fluid through the bloodstream to dilute the accumulation of sodium. The increase in the heart pumping increases blood pressure.
When researchers put mice on a high salt and high fat diet, not only did their blood pressure go up, but their gut microbiota changed as well. When the researchers gave the mice a probiotic for one week prior to going on the same diet, their gut microbiota remained the same, and… their blood pressure did not go up (32). A 2014 Meta-Analysis out of Hypertension had similar findings (17).
Probiotics have also been shown to positively impact Immune health (21), blood sugar and insulin sensitivity (15), post workout muscle damage (16), and more.
Now that you know that probiotics can impact your health in so many ways, how do you know which ones are best? Are the probiotics at the local convenience store the same as more expensive ones bought online?
Specific Strains that have been shown in research to have positive effects on health:
Lactobacillus Reuteri: (see Dr. Erdman’s research as well)
- L. reuteri DSM 17938 was found to improve lifespan, improve gut bacteria composition, and decrease inflammation (23).
- 5 days of supplementation with L. reuteri DSM 17938 decreased the duration of diarrhea and was well tolerated in children (23).
- 4 weeks of supplementation led to decrease in stomach pain frequency and intensity (23).
- 3 weeks of L. reuteri DSM 17938 was effective at treating infant colic (23).
- Meta-analysis of 32 studies (2,242 total patients) on L. reuteri DSM 17938 found consistent reduction in duration of crying time in colic (14).
Brand: BioGaia uses the patented L. reuteri DSM 17938 in their line of probiotic supplements. Their product line consists of:

- BioGaia Protectis, which contains 100 million live L. reuteri microorganisms, for general adult gut health.
- Biogaia Prodentis uses L. reuteri DSM 17938 in lozenge form to aid in restoring gum and oral health.
- BioGaia Protectis Baby Drops (with or without vitamin D) is recommended by pediatricians around the globe. Contains 100 million live L. reuteri as well.
- BioGaia Gastrus for gastrointestinal health contains the patented L. reuteri Gastrus which contains both L. reuteri DSM 17938 and L. reuteri ATCC PTA 6475.
- BioGaia Osfortis for bone health contains the patented L. reuteri ATCC PTA 6475 and vitamin D3.
For more info check out: BioGaia Probiotics – a world leading health care company
Bifidobacterium lactis HN019:
Studies on B. lactis HN019 and Immune Health
- Has been found to increase immune function and decrease inflammation (18).
- Improved body’s natural antioxidant defenses while decreasing inflammation associated with oxidative stress (2).
- Improved immune function in elderly subjects (13).
- Subjects taking B. lactis HN019 had greatest improvements in immune defense (4).
- Randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study found significant improvements in immune health and defenses after only 6 weeks of supplementing with B. lactis HN019 (1).
Brand: B. lactis HN019 is patented by HOWARU and found in brands including Poliquin Proflora Excellence.

HOWARU also contracts out to other supplement distributors allowing them to include their patented strains. Other Brands that you can find the HN019 strain include:
- Metagenics Ultra Flora
- NOW Foods Clinical GI Probiotic
- Hormone Synergy’s Probiotic Synergy
- Nature Made Advanced Dual Action
- Nature’s Way Fortify Daily Extra Strength
Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM:
- Decreased incidence of pediatric diarrhea and may aid in healthy digestion of lactose products (25).
- Along with B. lactic Bi-07, improved symptoms of IBS and other bowel disorders (24).
Brands:
- Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Adult Probiotics Once Daily Ultra
- NOW Respiratory Care Probiotic
- Nature’s Way Fortify Optima
- Thorne Research FloraSport 20B
Saccharomyces boulardii
- Broad positive impact on the immune system responses to viruses, bacteria, and more (27).
- Improvement of leaky gut syndrome by repairing and enhancing intestinal barrier integrity and function (28).
- Meta-analysis found decrease in IBS and H-pylori symptoms (20).
- Increased running speed and “at-fatigue” VO2Max (26).
Brands:
- NOW Supplements Saccharomyces Boulardii
- Jarrow Formulas Saccharomyces Boulardii + MOS
- Biotics Saccharomyces boulardii
- Klaire Labs Saccharomyces Boulardii
- Renew Life Adult Probiotic Ultimate Flora Saccharomyces boulardii
Lactobacillus casei
- L. casei can be found in the reproductive and gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals as well as in cheese, wine, and pickles (19).
- Has been shown to positively alter gut bacteria, improve immunity, enhance brain and intestinal barrier function, and symptoms of colitis, but only did so when taken with milk (19).
Brand: Innovia, by Italian company SOFAR, uses their trademark strain LP-DG (Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-1572) in improving intestinal bacteria composition, reducing inflammation, decreasing symptoms of bowel disorders.

SOFAR’s Eterolactis is the most prescribed probiotic by doctors in Italy and is regarded as one of the best probiotic supplement brands in the world. Innovia has two products, Liquid Fiber and Digestion, both in the form of micro-shots. You can get a 2 free samples from their site: Innovia Nectar: Probiotic Microshots
Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001:
- Early childhood supplementation was associated with significant reductions in allergic reactions including eczema and hay fever (31).
- Along with B. Longum BB536, improved microbiota composition in GI tract (29).
- Found to have protective effects against eczema in infants (30).
Brand: Culturelle uses the L. rhamnosus LGG strain in their product line. Their Ultimate Strength Probiotic contains 20 billion live cultures of L. rhamnosus GG, as well as the prebiotic Inulin for the bacteria to feed off.
They offer several different products for adults and children that you can find in many grocery store chains. Culturelle® | Probiotics Supplements for Digestive Support.
Lactobacillus Plantarum
- Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over human trial found that 80% of the genes stimulated by L. plantarum TIFN101 are related to immunity (5).
Brands:
- Thorne Research FloraPro-LP Probiotic
- Physicians Choice 60 Billion Probiotic
- Schwartz Probiotic 40 Billion CFU
- Jarrow Formulas Ideal Bowel Support
- Nature’s Bounty Probiotic GX
With so many supplement products out there on the market, how do you know which ones work and which ones do not? How do you know which ones are good quality and which ones are not?
Supplement Buying Tips
- You have heard about a supplement on a commercial or in conversation, or you have read about a supplement online or across social media.
- Go to google and type in: “the supplement name”, benefits, NCBI. This will bring you to the scientific studies on PubMed (the NIH’s online database). Click on the most relevant study. Over on the right hand side of the page you will see “Similar articles in PubMed” (shown below):
Similar articles in PubMed
- Market potential for probiotics.
- [Am J Clin Nutr. 2001]
- Non-dairy probiotic products.
- [Food Microbiol. 2010]
- Probiotics–the friendly bacteria with market potential in global market.
- [Pak J Pharm Sci. 2007]
- Probiotic bacteria: selective enumeration and survival in dairy foods.
- [J Dairy Sci. 2000]
- Discovering probiotic microorganisms: in vitro, in vivo, genetic and omics approaches.
- [Front Microbiol. 2015]
Click on the see all tab.
This will bring you to all similar studies on PubMed. You can organize these by best match, most recent, and publication date.
Use Examine.com
- Examine.com: Independent Analysis on Supplements & Nutrition Examine has put together the one of the most, if not the most, comprehensive database of studies on supplement ingredients. They have compiled nearly all the relevant literature on each ingredient/supplement and present it in a very easy to read manner. They provide you with:
- Summary of the ingredient (for example: Lactobacillus reuteri)
- How to take it (recommended dosage, active amounts, other details)
- The Human Effect Matrix (these are the studies done on humans)
- An easy to read chart that consists of:
Level of Evidence Outcome Magnitude of Effect Consistency of Results
Use Labdoor.com
Use Labdoor.com to verify the quality of most common brands. Labdoor: Supplement Ratings and Reviews. Currently they have 36 separate supplement categories in which they have rigorously tested for quality. They perform analytical chemistry assays on samples of each product at an FDA-registered lab. They measure for active ingredients and potential contaminants. They score these according to:
- Label Accuracy
- Product Purity
- Nutritional Value
- Ingredient Safety
- Projected Efficacy
Quick tip: Another way to ensure quality is to seek out Pharmaceutical Grade products. There are 3 grades of raw materials used in products:
- Pharmaceutical Grade
- Food Grade: meets standards for human consumption
- Feed Grade: meets standards for animal consumption
To achieve Pharmaceutical Grade, a product must be manufactured in an FDA registered facility that follow Certified Good Manufacturing Practices, and contains no fillers, dyes, or binders, and must be 99% pure.
What are the top probiotic supplements?
Of the brands tested on Labdoor.com, they currently have 8 brands that achieved an “A+, A, or A-” rating (keep in mind, these are only from the list of brands they tested):
A+ Culturelle Digestive Health Probiotic.
A+ Schiff Digestive Advantage Daily Probiotic.
A Trunature Digestive Probiotic.
A Ortho Molecular Products Ortho Biotic.
A Garden of Life Primal Defense Ultra Probiotic Formula.
A- Florastor.
A- Dr. Formulas Nexabiotic Advanced Multi-Probiotic.
A- Align Probiotic Supplement.
What are some good sources for natural probiotics?
- Kefir fermented milk drink.
- Icelandic or Greek Yogurt are good low carb, high quality fat options. Quick Tip: Look for the term “live active cultures” on the label.
- Kombucha: Spoonuniversity.com offers a simple guide to buying a quality Kombucha product:
- Make sure it is in a glass bottle vs plastic. When it is fermented in plastic, it can leach plastic into the drink.
- The list of ingredients should be short. They should be water, tea leaves, sugar, and SCOBY, with no artificial flavors or fillers.
- It should come in a dark bottle as light can damage the probiotic bacteria.
- Ideally, you want it to have Vitamin B listed on the label, as this ensures it was not pasteurized with heat.
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Pickles are known for their probiotic properties. But be careful, there are two types of pickles: ones made in vinegar and fermented pickles. The ones made in vinegar do not have anywhere near the bacteria composition as the fermented ones. Couple quick tips to picking out higher probiotic composition pickles:
- If it says vinegar on the label it more than likely was not fermented.
- Look in the refrigerated section for fermented pickles.
- Farmer’s market may be a good option.
- Gouda and Cottage Cheese: Look for live and/or active cultures on the label
- Sauerkraut. Look for Sauerkraut in the refrigerated section, as it is supposed to be alive. The Sauerkraut on the shelves is most likely dead and has ceased fermenting. As with pickles, you may want to avoid it if it has vinegar on the label.
- Traditional Buttermilk (non-cultured)
- Kimchi
- Miso
What are prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible dietary plant fibers that serve as food for friendly gut bacteria. By providing a food source, they increase healthy bacteria population, which in turn helps with immune function, digestion, energy, vitamin, nutrient production, and more.
What are some good sources for prebiotics?
- Raw Garlic Cloves
- Raw Asparagus
- Raw or Cooked Onions
- Pistachios
- Raw Almonds
- Lentils, split peas, beans, and chickpeas
- Chicory Root Powder
- Green Bananas
- Spinach
- Plantains
- Jerusalem Artichokes
- Apple Pectin
- Sweet Potato
- Yams
Do the cultures need to be alive to cultivate the gut?
Yes. By using the available science in human models, manufacturers can determine which strains survive, cultivate, and have a positive impact on desired outcomes. They can also test the strain in the lab to see if it can survive the different ph. levels of the stomach and upper GI tract.
Some manufacturers use enteric coatings or time release technology to ensure live delivery to the intestinal tract.
What is more important, the amount (billions) or quality of the strain?
100 billion live cultures of a strain that does not survive the acid in your stomach may not be a wise investment.
When is the best time to take a probiotic?
Keeping the above two questions in mind, the cultures need to survive the stomach acid and bile in order to cultivate in the intestinal tract. To ensure this delivery, taking a probiotic when our stomach acid levels are lowest may be a good option. Two things to keep in mind:
- If you have eaten, your body produces stomach acid to break down the food.
- Your stomach acid levels can be minimal in the morning before breakfast or prior to eating a meal during the day (22).
For more Workouts for Working People (The Ultimate Guide) people check out Part 1: How To Fit Exercise In When Working Full Time and Part 2: Best Tips On How To Improve Your Posture. Or, pick up a copy of the book Lifestyle Hack and Workouts for Working People on kindle or paperback today.
Thx for reading!
References
- Arunachalam et al. Enhancement of natural immune function by dietary consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis (HN019). European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 54(3); Pp 262-267. 2000.
- Bernini et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on inflammatory markers and oxidative stress in subjects with and without the metabolic syndrome. British Journal of Nutrition. 120(6); Pp 645-652. 2018.
- Biagi E, Brigidi P et al. The gut microbiota of centenarians: Signatures of longevity in the gut microbiota profile. Mechanisms of Aging and Development. 165; Pp 180-184. 2017.
- Chiang et al. Enhancing immunity by dietary consumption of a probiotic lactic acid bacterium (Bifidobacterium lactis HN019): optimization and definition of cellular immune responses. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 54(11); Pp 849-855. 2000.
- de Vos, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum Strains Can Enhance Human Mucosal and Systemic Immunity and Prevent Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Induced Reduction in T Regulatory Cells. Frontiers in Immunology. 8; Pp 1000. 2017.
- Erdman et al. Probiotic bacteria induce a “Glow of Health”. PLoS One. 10.1371. January 2013.
- Erdman S, Alm E, et al. Microbial reprogramming inhibits Western diet associated obesity. PLoS One. 8(7); Pp e68596. 2013
- Erdman et al. Probiotic microbes sustain youthful serum testosterone levels and testicular size in aging mice. PLoS One. 10.1371. January 2014.
- Erdman S, Alm E, et al. Beneficial Bacteria Stimulate Youthful Thyroid Gland Activity. Journal of Obesity and Weight Loss Therapy. 4; Pp 220. 2014.
- Erdman and Poutahidis. Gut bacteria and Cancer. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1856(1); Pp 86-90. 2015.
- Erdman S. Microbes and healthful longevity. Aging. 8(5); Pp 839-840. 2016.
- Frati et al. Allergy and the gastrointestinal system. Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 153(1); Pp 3-6. 2008.
- Gill et al. Enhancement of immunity in elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 74(6); Pp 833-839. 2001.
- Gutiérrez-Castrellón P, et al. Efficacy of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for infantile colic. Systematic review with network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 96(51); e9375. 2017.
- Hulston et al. Probiotic supplementation prevents high fat, over-feeding induced insulin resistance in human subjects. British Journal of Nutrition. 113(4); Pp 596-602. 2015.
- Jager et al. Effects of probiotic supplementation on markers of skeletal muscle damage, perceived recovery and athletic performance after an intense single leg training bout. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 12(1); Pp 36. 2015.
- Khalesi et al. Effect of probiotics on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension. 64(4); Pp 897-903. 2014.
- Liu et al. Adhesion and immunomodulatory effects of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on intestinal epithelial cells INT-407. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 16(18); Pp 2283-2290. 2010.
- McGee et al. Prolonged Faecal Excretion Following a Single Dose of Probiotic in Low Birth Weight Infants. Acta Paediatr. 99(10); Pp 1587-1588. 2010.
- McFarland L. Systematic review and meta-analysis of Saccharomyces boulardii in adult patients. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 16(18); Pp 2202-2222. 2010.
- Mengheri et al. Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice. Nutrition. 63-64; Pp 184-192. 2019.
- MOORE J and ENGLERT E. Circadian Rhythm of Gastric Acid Secretion in Man. Nature. 226; Pp 1261–1262. 1970.
- Mu Q, et al. Role of Lactobacillus reuteri in Human Health and Diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9; Pp 757. 2018.
- Ringel-Kulka et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobcillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactic Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional disorders: a double blind study. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 45(6); Pp 518-525. 2011.
- Sanders and Klaenhammer. Invited review: the scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic. Journal of Dairy Sciences. 84(2); Pp 319-331. 2001.
- Soares et al. Supplementation with Saccharomyces boulardii increases the maximal oxygen consumption and maximal aerobic speed attained by rats subjected to an incremental speed exercise. Nutrients. 11(10); Pp E2352. 2019.
- Stier and Bischoff. Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 influences the gut-associated immune system. MMW Fortschr Med. 159(5); Pp 1-6. 2017.
- Terciolo et al. Beneficial effects of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on clinical disorders associated with intestinal barrier disruption. Clinical Experiences in Gastroenterology. 12; Pp 67-82. 2019.
- Toscano et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Bifidobacterium longum BB536 on the healthy gut microbiota composition at phyla and species level: A preliminary study. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 23(15); Pp 2696-2704. 2017.
- Wickens et al. A protective effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 against eczema in the first 2 years of life persists to age 4 years. Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 42(7); Pp 1071-1079. 2012.
- Wickens et al. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in early life on the cumulative prevalence of allergic disease to 11 years. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 29(8); Pp 808-814. 2018.
- Wilck N, Muller, Alm E, et al. Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates Th17 axis and disease. Nature. 551(7682); Pp 585-589. 2017.



